When someone asks you “What is this book about?”, there are a few ways you can answer. There’s “plot,” which refers to the literal events in the book, and there’s “character,” which refers to the people in the book and the struggles they overcome. Finally, there are themes in literature that correspond with the work’s topic and message. But what is theme in literature?
The theme of a story or poem refers to the deeper meaning of that story or poem. All works of literature contend with certain complex ideas, and theme is how a story or poem approaches these ideas.
There are countless ways to approach the theme of a story or poem, so let’s take a look at some theme examples and a list of themes in literature. We’ll discuss the differences between theme and other devices, like theme vs moral and theme vs topic. Finally, we’ll examine why theme is so essential to any work of literature, including to your own writing.
But first, what is theme? Let’s explore what theme is—and what theme isn’t.
Common Themes in Literature: Contents
Theme Definition: What is Theme?
Theme describes the central idea(s) that a piece of writing explores. Rather than stating this theme directly, the author will look at theme using the set of literary tools at their disposal. The theme of a story or poem will be explored through elements like characters, plot, settings, conflict, and even word choice and literary devices.
Theme definition: the central idea(s) that a piece of writing explores.
That said, theme is more than just an idea. It is also the work’s specific vantage point on that idea. In other words, a theme is an idea plus an opinion: it is the author’s specific views regarding the central ideas of the work.
All works of literature have these central ideas and opinions, even if those ideas and opinions aren’t immediate to the reader.
Justice, for example, is a literary theme that shows up in a lot of classical works. To Kill a Mockingbird contends with racial justice, especially at a time when the U.S. justice system was exceedingly stacked against African Americans. How can a nation call itself just when justice is used as a weapon?
By contrast, the play Hamlet is about the son of a recently-executed king. Hamlet seeks justice for his father and vows to kill Claudius—his father’s killer—but routinely encounters the paradox of revenge. Can justice really be found through more bloodshed?
What is theme? An idea + an opinion.
Clearly, these two works contend with justice in unrelated ways. All themes in literature are broad and open-ended, allowing writers to explore their own ideas about these complex topics.
20 Common Themes in Literature
Let’s look at some common themes in literature. The ideas presented within this list of themes in literature show up in novels, memoirs, poems, and stories throughout history.
| Theme | Theme Definition | Theme Examples |
| Circle of Life | What comes around, goes around. The Circle of Life dwells on life’s transience and impermanence: how death isn’t death, just an evolution. |
|
| Coming of Age | Also known as a bildungsroman, Coming of Age involves the intense experiences of growing up, and how these experiences shape the future of the protagonist. |
|
| Faith vs Doubt | Whether it’s faith in God, other people, or the protagonist’s own self, believing isn’t easy—but is it worth doing anyway? |
|
| Family | Many families are connected by blood, but to overcome certain obstacles, literary families must strengthen their ties to each other. |
|
| Fate vs Free Will | How much of our actions are decided by fate, and how much does free will really control? |
|
| Good vs Evil | One can argue that every story is about good vs evil, assuming the story has a protagonist and antagonist. Still, good and evil are in eternal conflict with each other, so writers must document how this conflict evolves. |
|
| Hubris | Hubris refers to excessive self-confidence and the terrible decisions that arise from it. Many works of literature explore hubris as man’s defiance of God/the gods, or else man himself playing God. |
|
| Identity | At some point in their life, the protagonist asks the question: who am I?
Additionally, “Identity” refers to the qualities that make one person distinct from another. How much of a difference exists between you and I? |
|
| Justice | What makes a society just? What are the proper consequences for people who do the wrong thing? Who is best equipped to dispense justice? Are we collectively responsible for each other’s actions? |
|
| Loneliness | Loneliness affects the way people think, act, and view the world. The theme of loneliness charts how certain characters contend with their loneliness, and whether man can survive this disconnection from others. |
|
| Man vs Nature | Man’s natural inclination is to dominate the land, but nature has its own means of survival. |
|
| Man vs Self | Sometimes, the protagonist is their own adversary. In order to overcome certain challenges, the protagonist must first overcome their own internal conflicts. |
|
| Man vs Society | When the story’s antagonist is society-at-large, the protagonist must convince the world that it’s sick—or else die trying. Some protagonists also try to escape society altogether. |
|
| Power and Corruption | Power corrupts, and absolute power corrupts absolutely. This theme is often closely related to “Man vs Society.” Additionally, “Power” can refer to a person’s political leadership, personal wealth, physical prowess, etc. |
|
| Pursuit of Love | Love makes the world go round, but it’s not always easy to find. Whether it’s romantic, familial, or platonic love, there’s much to be said about love’s pursuit—and the conflict that comes from pursuing it. |
|
| Revenge | When someone wrongs you or the people you love, revenge is tempting. But, is revenge worth it? Can revenge beget justice? And how far is too far? |
|
| Sacrificial Love | When you truly love someone, you’re willing to sacrifice everything for them. Sacrifice is a component of all themes concerning love, though this is especially true for stories about motherly love. |
|
| Survival | When survival is at stake, people discover the limits of their own power. The literary theme of survival applies to stories about being lost in the wilderness, but it also applies to stories about the survival of ideas, groups, and humanity-at-large. |
|
| The Environment | Whether it’s because of technology, climate change, or our increasingly online world, man’s relationship to the environment is ever-evolving. Themes in literature concerning the environment often coincide with “man vs nature.” |
|
| War | Mankind has been at war with itself since the dawn of civilization. The causes of war, as well as its impacts on society, are topics of frequent musing by writers—especially writers who have been at war themselves. |
|
Theme Examples in Literature
Let’s take a closer look at how writers approach and execute theme. Themes in literature are conveyed throughout the work, so while you might not have read the books in the following theme examples, we’ve provided plot synopses and other relevant details where necessary. We analyze the following:
- Power and Corruption in the novel Animal Farm
- Loneliness in the short story “A Clean, Well-Lighted Place”
- Love in the poem “How Do I Love Thee”
Theme Examples: Power and Corruption in the Novel Animal Farm
At its simplest, the novel Animal Farm by George Orwell is an allegory that represents the rise and moral decline of Communism in Russia. Specifically, the novel uncovers how power corrupts the leaders of populist uprisings, turning philosophical ideals into authoritarian regimes.
Most of the characters in Animal Farm represent key figures during and after the Russian Revolution. On an ailing farm that’s run by the negligent farmer Mr. Jones (Tsar Nicholas II), the livestock are ready to seize control of the land. The livestock’s discontent is ripened by Old Major (Karl Marx/Lenin), who advocates for the overthrow of the ruling elite and the seizure of private land for public benefit.
After Old Major dies, the pigs Napoleon (Joseph Stalin) and Snowball (Leon Trotsky) stage a revolt. Mr. Jones is chased off the land, which parallels the Russian Revolution in 1917. The pigs then instill “Animalism”—a system of government that advocates for the rights of the common animal. At the core of this philosophy is the idea that “all animals are equal”—an ideal that, briefly, every animal upholds.
Initially, the Animalist Revolution brings peace and prosperity to the farm. Every animal is well-fed, learns how to read, and works for the betterment of the community. However, when Snowball starts implementing a plan to build a windmill, Napoleon drives Snowball off of the farm, effectively assuming leadership over the whole farm. (In real life, Stalin forced Trotsky into exile, and Trotsky spent the rest of his life critiquing the Stalin regime until he was assassinated in 1940.)
Napoleon’s leadership quickly devolves into demagoguery, demonstrating the corrupting influence of power and the ways that ideology can breed authoritarianism. Napoleon uses Snowball as a scapegoat for whenever the farm has a setback, while using Squealer (Vyacheslav Molotov) as his private informant and public orator.
Eventually, Napoleon changes the tenets of Animalism, starts walking on two legs, and acquires other traits and characteristics of humans. At the end of the novel, and after several more conflicts, purges, and rule changes, the livestock can no longer tell the difference between the pigs and humans.
Themes in Literature: Power and Corruption in Animal Farm
So, how does Animal Farm explore the theme of “Power and Corruption”? Let’s analyze a few key elements of the novel.
Plot: The novel’s major plot points each relate to power struggles among the livestock. First, the livestock wrest control of the farm from Mr. Jones; then, Napoleon ostracizes Snowball and turns him into a scapegoat. By seizing leadership of the farm for himself, Napoleon grants himself massive power over the land, abusing this power for his own benefit. His leadership brings about purges, rule changes, and the return of inequality among the livestock, while Napoleon himself starts to look more and more like a human—in other words, he resembles the demagoguery of Mr. Jones and the abuse that preceded the Animalist revolution.
Thus, each plot point revolves around power and how power is wielded by corrupt leadership. At its center, the novel warns the reader of unchecked power, and how corrupt leaders will create echo chambers and private militaries in order to preserve that power.
Characters: The novel’s characters reinforce this message of power by resembling real life events. Most of these characters represent real life figures from the Russian Revolution, including the ideologies behind that revolution. By creating an allegory around Lenin, Trotsky, Stalin, and the other leading figures of Communist Russia’s rise and fall, the novel reminds us that unchecked power foments disaster in the real world.
Literary Devices: There are a few key literary devices that support the theme of Power and Corruption. First, the novel itself is a “satirical allegory.” “Satire” means that the novel is ridiculing the behaviors of certain people—namely Stalin, who instilled far-more-dangerous laws and abuses that created further inequality in Russia/the U.S.S.R. While Lenin and Trotsky had admirable goals for the Russian nation, Stalin is, quite literally, a pig.
Meanwhile, “allegory” means that the story bears symbolic resemblance to real life, often to teach a moral. The characters and events in this story resemble the Russian Revolution and its aftermath, with the purpose of warning the reader about unchecked power.
Finally, an important literary device in Animal Farm is symbolism. When Napoleon (Stalin) begins to resemble a human, the novel suggests that he has become as evil and negligent as Mr. Jones (Tsar Nicholas II). Since the Russian Revolution was a rejection of the Russian monarchy, equating Stalin to the monarchy reinforces the corrupting influence of power, and the need to elect moral individuals to posts of national leadership.
Theme Examples: Loneliness in “A Clean, Well-Lighted Place”
Ernest Hemingway’s short story “A Clean, Well-Lighted Place” is concerned with the theme of loneliness. You can read this short story here. Content warning for mentions of suicide.
There are very few plot points in Hemingway’s story, so most of the story’s theme is expressed through dialogue and description. In the story, an old man stays up late drinking at a cafe. The old man has no wife—only a niece that stays with him—and he attempted suicide the previous week. Two waiters observe him: a younger waiter wants the old man to leave so they can close the cafe, while an older waiter sympathizes with the old man. None of these characters have names.
The younger waiter kicks out the old man and closes the cafe. The older waiter walks to a different cafe and ruminates on the importance of “a clean, well-lighted place” like the cafe he works at.
Themes in Literature: Loneliness in “A Clean, Well-Lighted Place”
Hemingway doesn’t tell us what to think about the old man’s loneliness, but he does provide two opposing viewpoints through the dialogue of the waiters.
The younger waiter has the hallmarks of a happy life: youth, confidence, and a wife to come home to. While he acknowledges that the old man is unhappy, he also admits “I don’t want to look at him,” complaining that the old man has “no regard for those who must work.” The younger waiter “did not wish to be unjust,” he simply wanted to return home.
The older waiter doesn’t have the privilege of turning away: like the old man, he has a house but not a home to return to, and he knows that someone may need the comfort of “a clean and pleasant cafe.”
The older waiter, like Hemingway, empathizes with the plight of the old man. When your place of rest isn’t a home, the world can feel like a prison, so having access to a space that counteracts this feeling is crucial. What kind of a place is that? The older waiter surmises that “the light of course” matters, but the place must be “clean and pleasant” too. Additionally, the place should not have music or be a bar: it must let you preserve the quiet dignity of yourself.
Lastly, the older waiter’s musings about God clue the reader into his shared loneliness with the old man. In a stream of consciousness, the older waiter recites traditional Christian prayers with “nada” in place of “God,” “Father,” “Heaven,” and other symbols of divinity. A bartender describes the waiter as “otro locos mas” (translation: another crazy), and the waiter concludes that his plight must be insomnia.
This belies the irony of loneliness: only the lonely recognize it. The older waiter lacks confidence, youth, and belief in a greater good. He recognizes these traits in the old man, as they both share a need for a clean, well-lighted place long after most people fall asleep. Yet, the younger waiter and the bartender don’t recognize these traits as loneliness, just the ramblings and shortcomings of crazy people.
Does loneliness beget craziness? Perhaps. But to call the waiter and old man crazy would dismiss their feelings and experiences, further deepening their loneliness.
Loneliness is only mentioned once in the story, when the young waiter says “He’s [the old man] lonely. I’m not lonely. I have a wife waiting in bed for me.” Nonetheless, loneliness consumes this short story and its older characters, revealing a plight that, ironically, only the lonely understand.
Theme Examples: Love in the Poem “How Do I Love Thee”
Let’s turn towards brighter themes in literature: namely, love in poetry. Elizabeth Barrett Browning’s poem “How Do I Love Thee” is all about the theme of love.
I love thee to the depth and breadth and height
My soul can reach, when feeling out of sight
For the ends of being and ideal grace.
I love thee to the level of every day’s
Most quiet need, by sun and candle-light.
I love thee freely, as men strive for right.
I love thee purely, as they turn from praise.
I love thee with the passion put to use
In my old griefs, and with my childhood’s faith.
I love thee with a love I seemed to lose
With my lost saints. I love thee with the breath,
Smiles, tears, of all my life; and, if God choose,
I shall but love thee better after death.
Themes in Literature: Love in “How Do I Love Thee”
Browning’s poem is a sonnet, which is a 14-line poem that often centers around love and relationships. Sonnets have different requirements depending on their form, but between lines 6-8, they all have a volta—a surprising line that twists and expands the poem’s meaning.
Let’s analyze three things related to the poem’s theme: its word choice, its use of simile and metaphor, and its volta.
Word Choice: Take a look at the words used to describe love. What do those words mean? What are their connotations? Here’s a brief list: “soul,” “ideal grace,” “quiet need,” “sun and candle-light,” “strive for right,” “passion,” “childhood’s faith,” “the breath, smiles, tears, of all my life,” “God,” “love thee better after death.”
These words and phrases all bear positive connotations, and many of them evoke images of warmth, safety, and the hearth. Even phrases that are morose, such as “lost saints” and “death,” are used as contrasts to further highlight the speaker’s wholehearted rejoicing of love. This word choice suggests an endless, benevolent, holistic, all-consuming love.
Simile and Metaphor: Similes and metaphors are comparison statements, and the poem routinely compares love to different objects and ideas. Here’s a list of those comparisons:
The speaker loves thee:
- To the depths of her soul.
- By sun and candle light—by day and night.
- As men strive to do the right thing (freely).
- As men turn from praise (purely).
- With the passion of both grief and faith.
- With the breath, smiles, and tears of her entire life.
- Now in life, and perhaps even more after death.
The speaker’s love seems to have infinite reach, flooding every aspect of her life. It consumes her soul, her everyday activities, her every emotion, her sense of justice and humility, and perhaps her afterlife, too. For the speaker, this love is not just an emotion, an activity, or an ideology: it’s her existence.
Volta: The volta of a sonnet occurs in the poem’s center. In this case, the volta is the lines “I love thee freely, as men strive for right. / I love thee purely, as they turn from praise.”
What surprising, unexpected comparisons! To the speaker, love is freedom and the search for a greater good; it is also as pure as humility. By comparing love to other concepts, the speaker reinforces the fact that love isn’t just an ideology, it’s an ideal that she strives for in every word, thought, and action.
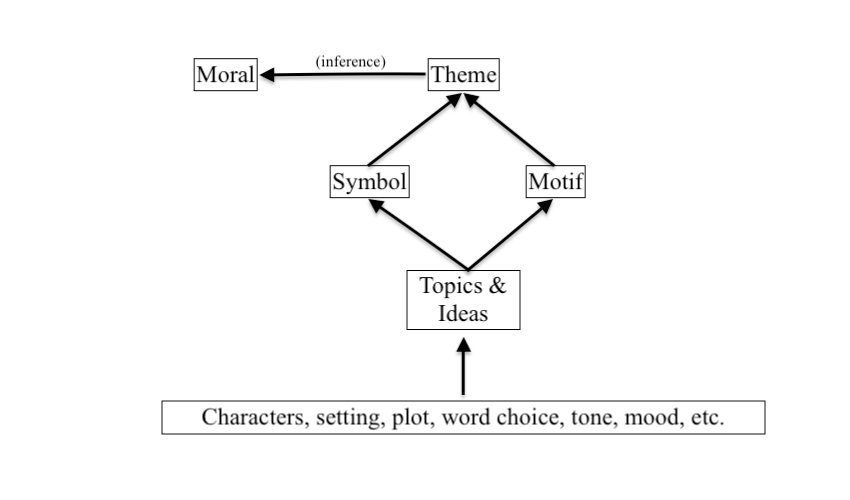
Themes in Literature: A Hierarchy of Ideas
“Theme” is part of a broader hierarchy of ideas. While the theme of a story encompasses its central ideas, the writer also expresses these ideas through different devices.
You may have heard of some of these devices: motif, moral, topic, etc. What is motif vs theme? What is theme vs moral? These ideas interact with each other in different ways, which we’ve mapped out below.
Theme vs Topic
The “topic” of a piece of literature answers the question: What is this piece about? In other words, “topic” is what actually happens in the story or poem.
You’ll find a lot of overlap between topic and theme examples. Love, for instance, is both the topic and the theme of Elizabeth Barrett Browning’s poem “How Do I Love Thee.”
The difference between theme vs topic is: topic describes the surface level content matter of the piece, whereas theme encompasses the work’s apparent argument about the topic.
Topic describes the surface level content matter of the piece, whereas theme encompasses the work’s apparent argument about the topic.
So, the topic of Browning’s poem is love, while the theme is the speaker’s belief that her love is endless, pure, and all-consuming.
Additionally, the topic of a piece of literature is definitive, whereas the theme of a story or poem is interpretive. Every reader can agree on the topic, but many readers will have different interpretations of the theme. If the theme weren’t open-ended, it would simply be a topic.
Theme vs Motif
A motif is an idea that occurs throughout a literary work. Think of the motif as a facet of the theme: it explains, expands, and contributes to themes in literature. Motif develops a central idea without being the central idea itself.
Motif develops a central idea without being the central idea itself.
In Animal Farm, for example, we encounter motif when Napoleon the pig starts walking like a human. This represents the corrupting force of power, because Napoleon has become as much of a despot as Mr. Jones, the previous owner of the farm. Napoleon’s anthropomorphization is not the only example of power and corruption, but it is a compelling motif about the dangers of unchecked power.
Learn more about motifs here:
Theme vs Moral
The moral of a story refers to the story’s message or takeaway. What can we learn from thinking about a specific piece of literature?
The moral is interpreted from the theme of a story or poem. Like theme, there is no single correct interpretation of a story’s moral: the reader is left to decide how to interpret the story’s meaning and message.
For example, in Hemingway’s “A Clean, Well-Lighted Place,” the theme is loneliness, but the moral isn’t quite so clear—that’s for the reader to decide. My interpretation is that we should be much more sympathetic towards the lonely, since loneliness is a quiet affliction that many lonely people cannot express.
Great literature does not tell us what to think, it gives us stories to think about.
However, my interpretation could be miles away from yours, and that’s wonderful! Great literature does not tell us what to think, it gives us stories to think about, and the more we discuss our thoughts and interpretations, the more we learn from each other.
Why Themes in Literature Matter
The theme of a story affects everything else: the decisions that characters make, the mood that words and images build, the moral that readers interpret, etc. Recognizing how writers utilize various themes in literature will help you craft stronger, more nuanced works of prose and poetry.
“To produce a mighty book, you must choose a mighty theme.” —Herman Melville
Whether a writer consciously or unconsciously decides the themes of their work, theme in literature acts as an organizing principle for the work as a whole. For writers, theme is especially useful to think about in the process of revision: if some element of your poem or story doesn’t point towards a central idea, it’s a sign that the work is not yet finished.
Moreover, literary themes give the work stakes. They make the work stand for something. Remember that our theme definition is an idea plus an opinion. Without that opinion element, a work of literature simply won’t stand for anything, because it is presenting ideas in the abstract without giving you something to react to. The theme of a story or poem is never just “love” or “justice,” it’s the author’s particular spin and insight on those themes. This is what makes a work of literature compelling or evocative. Without theme, literature has no center of gravity, and all the words and characters and plot points are just floating in the ether.
Should I Decide the Theme of a Story or Poem in Advance?
You can, though of course it depends on the actual story you want to tell. Some writers certainly start with a theme. You might decide you want to write a story about themes like love, family, justice, gender roles, the environment, or the pursuit of revenge.
From there, you can build everything else: plot points, characters, conflicts, etc. Examining themes in literature can help you generate some strong story ideas!
Nonetheless, theme is not the only way to approach a creative writing project. Some writers start with plot, others with character, others with conflicts, and still others with just a vague notion of what the story might be about. You might not even realize the themes in your work until after you finish writing it.
You certainly want your work to have a message, but deciding what that message is in advance might actually hinder your writing process. Many writers use their poems and stories as opportunities to explore tough questions, or to arrive at a deeper insight on a topic. In other words, you can start your work with ideas, and even opinions on those ideas, but don’t try to shoehorn a story or poem into your literary themes. Let the work explore those themes. If you can surprise yourself or learn something new from the writing process, your readers will certainly be moved as well.
So, experiment with ideas and try different ways of writing. You don’t have to think about the theme of a story right away—but definitely give it some thought when you start revising your work!
Develop Great Themes at Writers.com
As writers, it’s hard to know how our work will be viewed and interpreted. Writing in a community can help. Whether you join the Writers.com Community or enroll in one of our upcoming courses, we have the tools and resources to sharpen your writing.


Sean Glatch,Thank you very much for your discussion on themes. It was enlightening and brought clarity to an abstract and sometimes difficult concept to explain and illustrate. The sample stories and poem were appreciated too as they are familiar to me.
High School Language Arts Teacher
Hi Stephanie, I’m so glad this was helpful! Happy teaching 🙂
Wow!!! This is the best resource on the subject of themes that I have ever encountered and read on the internet. I just bookmarked it and plan to use it as a resource for my teaching. Thank you very much for publishing this valuable resource.
Hi Marisol,
Thank you for the kind words! I’m glad to hear this article will be a useful resource. Happy teaching!
Warmest,
Sean
builders beams bristol
What is Theme? A Look at 20 Common Themes in Literature | writers.com
Hello!
This is a very informative resource. Thank you for sharing.
farrow and ball pigeon
What is Theme? A Look at 20 Common Themes in Literature | writers.com
Thank you so much for this. It helped me understand these literary pieces mentioned more. You are really great at explaining things 🫶🏻
This presentation is excellent and of great educational value. I will employ it already in my thesis research studies.
John
Never before communicated with you!
Brilliant! Thank you.
[…] THE MOST COMMON THEMES IN LITERATURE […]
marvellous. thumbs up
Thank you. Very useful information.
found everything in themes. thanks. so much
In college I avoided writing classes and even quit a class that would focus on ‘Huck Finn’ for the entire semester. My idea of hell. However, I’ve been reading and learning from the writers.com articles, and I want to especially thank Sean Glatch who writes in a way that is useful to aspiring writers like myself.
You are very welcome, Anne! I’m glad that these resources have been useful on your writing journey.
Warmest,
Sean
Thank you very much for this clear and very easy to understand teaching resources.
Hello there. I have a particular question.
Can you describe the exact difference of theme, issue and subject?
I get confused about these.
Thanks
I love how helpful this is i will tell my class about it!
[…] https://writers.com/common-themes-in-literature […]
Love your interpretation and presentation of these elements of writing. I’m trying to help my JH students understand WHY we need theme. This was helpful. Thank you!
[…] (Sources: SparkNotes, LeverageEdu, Writers.com) […]
[…] have been thinking about themes in literature this week, and found this article by Sean Glatch interesting. Glatch outlines 20 themes, although there are others. I began to […]